Capacitive Touch Screen vs Resistive Touchscreen: Which is Right for You?
Exploring the Basics of Touchscreen Technology
What is a Capacitive Touch Screen?
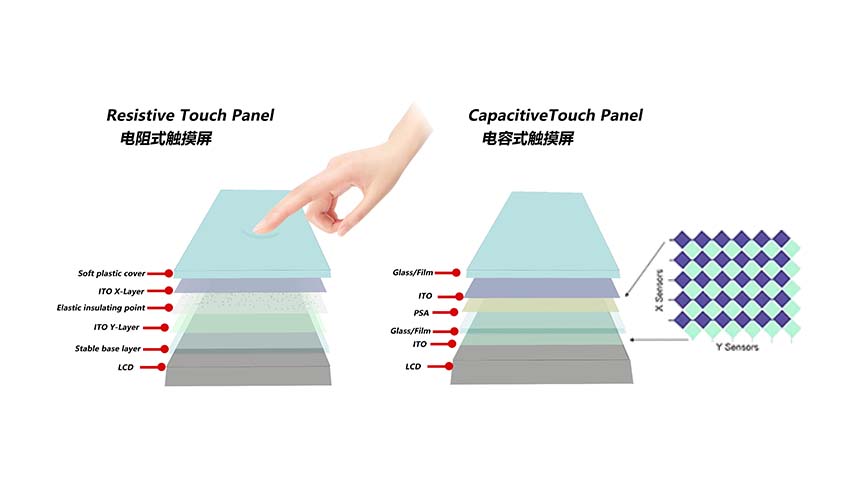
A capacitive touch screen uses capacitance to sense the conductive touch of a human finger or a conductive, grounded object. It uses the human skin’s natural conductivity to know when it has been touched. Easy to operate, the screens are sensitive and accurate which makes them perfect for uses that require sensitive touch input.
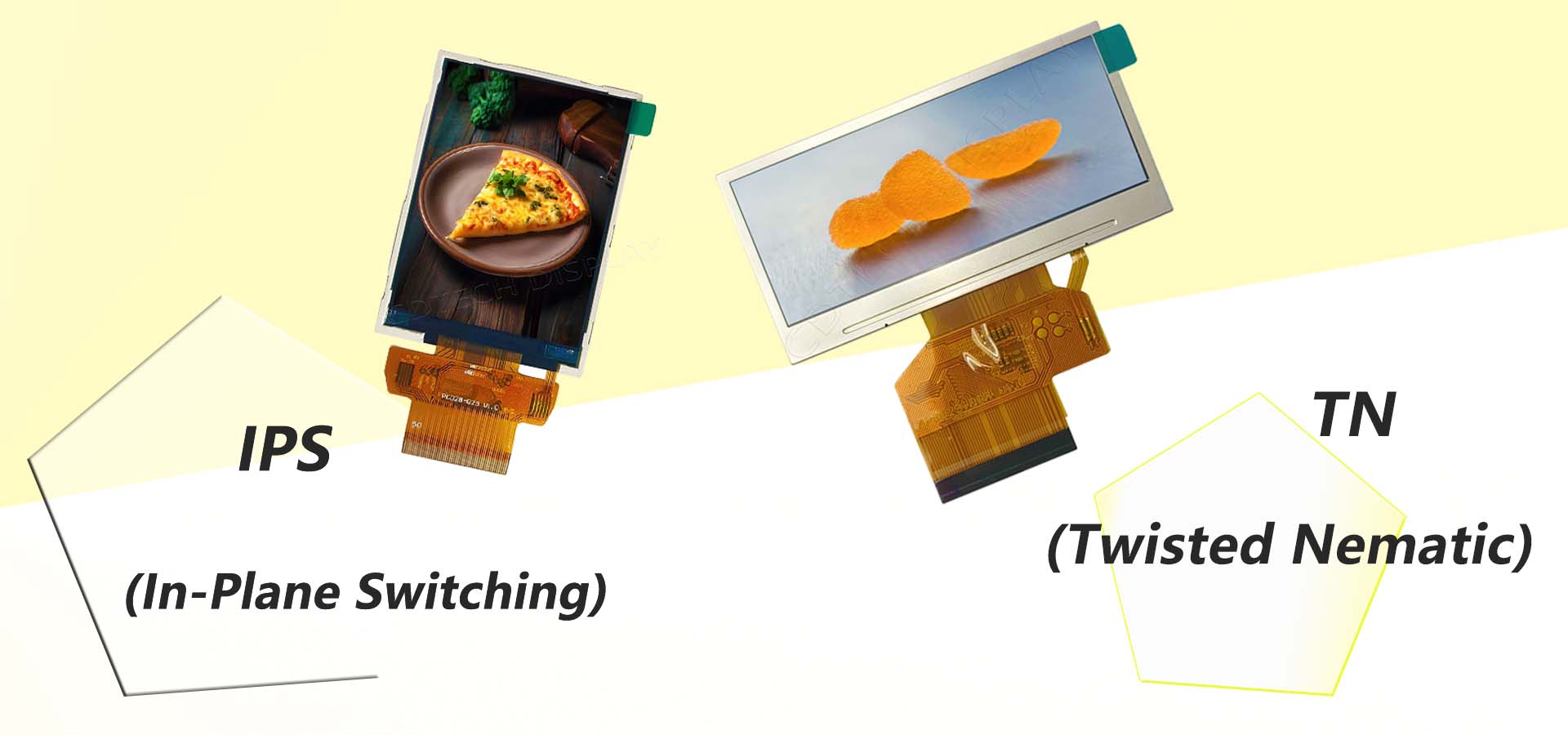
CDTech products with capacitive touch screens include the 4.0″ IPS Display, 480×480, 300 Nits with Capacitive Touch Panel Optical bonded and the 7.0″ Sunlight Readable IPS Display, 1024×600, 1500 Nits with Capacitive Touch Panel Optical bonded. These products are designed to deliver accurate and dependable touch performance.
What is a Resistive Touchscreen?
A resistive touchscreen works by sensing the pressure applied on top of the screen. They are made up of two bendable layers separated by a gap that registers contact when they are squeezed together. Such a touchscreen is typically used in environments where gloves or stylus writing are the norm, like industrial and medical ones. An example of the technology found in CDTech’s 7.0″ TN Display, 800×480, 400 Nits, with Resistive Touch Panel suitable for a variety of applications.
Comparing Capacitive and Resistive Touchscreens
Sensitivity and Accuracy
Capacitive touch screens are typically more sensitive and precise than resistive touchscreens. The registers can even detect light contacts, such as fingers or conductive styluses without needing to physically push into the screen. A good example of this is the 5.0″ IPS Display, 800×480, 400 Nits with Capacitive Touch Panel Air bonded from CDTech.
Unlike resistive screens, which need pressure to register input, are less sensitive to light touches, but can be used with fingers, gloves, and styli. This makes them a good selection for conditions in which accuracy is not as important however longevity under many circumstances is required. This property makes them ideal for applications where accuracy is not the most important factor but where harsh conditions can be expected.
Durability and Maintenance
When it comes to durability, both capacitive and resistive touchscreens offer different factors to consider. CDTech LCD goods that can last a long term are high-quality quality reliable; customers could easily rely on them, and the breakdown rate is significantly less. But correct operation and storage methods should be in place: the FPC gold fingers cannot be directly contacted with hands to be oxidized, so it is suggested to use anti-static gloves and wear anti-static finger cots during operation, and the grounded methods should also be in place.
Capacitive screens have a protective glass layer on top making it more scratch resistant. Though they have a higher tendency to break from knife or shock than resistive displays. But they can be more prone to damage from sharp items or impacts than resistive screens.
Cost Considerations
This cost aspect is one of the most important factors in the option between capacitive and resistive touchscreen technology. Touch screens can also be a bit pricey, and in general tend to fall into the pricey side of the spectrum, largely due to the complexity of the technology involved and the expensive materials used in mass production (e.g. glass). This is why products such as CDTech 7.0″ IPS Display, 1024 x 600, 420 Nits with Capacitive Touch Panel Optical bonded are also higher end.
Due to its simple technology that works on pressure and not on conductivity, resistive screens tend to be less expensive. As such, these so-called low-end chips are more appealing for cost-sensitive projects or in applications where cost savings are preferred to advanced capabilities. This can make them ideal for projects or applications that need to be budget-wise or save costs more than getting feature-rich capabilities.
Choosing the Right Touchscreen for Your Needs
Identifying Your Use Case
Choosing between capacitive and resistive touchscreen and knowing your use case is paramount. Take note of the environment where the touchscreen will be used. If, on the other hand, your application needs more accuracy and sensitivity, e.g., for consumer electronics or professional devices a capacitive touchscreen may be a better choice. One example is the CDTech 4.0 IPS Display, Square Type 480×480, 300 Nits with Capacitive Touch Panel Optical bonded, which features high-level sensitivity and accuracy – perfect for any application requiring accurate touches.
However, if your application is intended for tougher environments where people are expected to wear gloves or use a stylus — like an industrial environment, for example, or medical equipment — a resistive touchscreen may be the way to go. One great option for such a variety of input is the CDTech 7.0″ TN Display, 800×480, 400 Nits with a Resistive Touch Panel.
Evaluating User Experience
Finally, the most important point when choosing a touchscreen is user experience. Capacitive screens offer a more fluid and responsive interface since can detect multiple points of contact at the same time. Floated touch gesturing is a neat touch that helps to improve the user experience, enabling pinch-to-zoom and multi-finger swiping.
While generally much less responsive than their capacitive counterparts, resistive screens provide more reliable performance when users may need to use the device with non-conductive materials such as gloves. This allows them to be used where user interaction is minimal but ruggedness in the field is high.
Introducing CDTech: Innovative Solutions in Touchscreen Technology
Overview of CDTech’s Offerings
CDTech is a seasoned touch technology solution provider dealing in innovative solutions for various applications. Their products include capacitive and resistive touchscreens to meet diverse application requirements and the right offering for cost-sensitive consumer applications to industrial equipment used in harsh working conditions.
Other Products by CDTech
In addition to their well-known capacitive and resistive touchscreen offerings, CDTech also offers other high-end display technologies. Take the example of the 7.0″ Sunlight Readable IPS Display, 1024×600, 1500 Nits with Capacitive Touch Panel Optical bonded ideal for outdoor applications because sunlight readability and high brightness are the most critical factors for outdoor uses.
With insight into your specific requirements and the full portfolio of CDTech products including their industry-leading capacitive devices, you will be able to determine which technology best suits your touchscreen, ensuring optimal performance targeted directly at your unique application needs.
FAQ
Q: How does a capacitive touchscreen work?
A: These touchscreens operate by detecting the electrical properties of the human body. It has a conductive layer (generally with the ITO, Indium Tim Oxide) that forms an electrostatic field over the surface and touches the surface to disrupt the field and by that, the point of contact is located by the device.
Q: Which touchscreen type is more durable in harsh environments?
A: A: In a broad sense, the resistive touchscreen has a mechanic layered construction that makes it more rugged in nasty environments (dust, moisture, or bulk gloves), while the capacitive screen has a mechanic stacked structure so it usually makes it clear and scratch resistant.
Q: Can resistive touchscreens support multi-touch gestures?
A: No, resistive touchscreens typically only support single-touch input due to their pressure-based mechanism. Capacitive screens, however, can easily handle multi-touch gestures like pinch-to-zoom.
Q: What are the cost differences between capacitive and resistive touchscreens?
A: For basic applications, resistive touchscreens tend to be cheaper, but once you start factoring in performance factors like the technology and the high transparency used in these systems for better display quality, capacitive kind of skate through a price hike.
Q: Which touchscreen is better for outdoor visibility?
A: Capacitive touchscreens perform better in direct sunlight because they often use anti-glare coatings and have higher light transmission. Resistive screens may struggle with reflectivity in bright environments.


 2025-03-11
2025-03-11  11:50
11:50